Previous Page | Right click this page to print.
Unit 9
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Sexually Transmitted Infection
- “STD”…. “Venereal Disease”
- These terms may all be used synonymously. The term STI is the current terminology used by many health professionals. This terminology helps to decrease the stigma associated with the word “disease”. You may have also heard the word venereal disease to describe STIs.
- Defined
- Infections contracted through sexual contact with an infected person.
- “Sexual contact” = Sexual practices in which semen, vaginal secretions or blood contact mucous membranes. (e.g., genital area, rectum, mouth)
- Over 25 different diseases
- STIs are among the most common contagious diseases in the US
STI Epidemic
- 1/6 American Adults has an STI
- This is a statistic from the textbook. It is somewhat conservative, as some studies indicate up to 1/3 American adults having an STI.
- 86% of all STIs occur among 15-29 year-olds
- 50% of Americans will contract an STI by age 30
Reasons Why STIs Are So Prevalent
- Many have no symptoms
- Changing trends in contraception
- IE: Birth control pills
- Sexual Revolution 1960’s
- Earlier sexual activity
- Casual attitudes
- Greater # of partners
- Social stigma
- STIs are not cool, sexy or fun to talk about. Individuals with an STI may fear social isolation, relationship problems, or being seen as ‘dirty’. The more an individual feels he/she will be thought poorly of, the less likely the individual will be to admit there is a problem, or to seek treatment.
- Social pressure
- There is a perception that everyone out there is having sex… this is not true!!! Images we see in the media and pressure from friends may lead us to believe sex is necessary to fit in.
- Denial
Common Myths
- If your partner doesn't have symptoms, you’re safe
- You can always tell if you have an STI
- If your symptoms go away on their own, you’re cured
High Risk Behaviors
- Unprotected sex
- Vaginal, Anal or Oral
- This includes giving or receiving vaginal sex without a condom, anal sex without a condom, oral-anal contact (rimming) without a barrier (dental dam), oral-vaginal or oral-penile contact without a barrier (dental dam or condom), contact with your partners blood, sharing sex toys with out cleaning or using a new condom
- Multiple Partners
- Or persons who have had multiple partners!
- Alcohol or Drug use which reduces inhibitions
General Signs & Symptoms
- Sores, bumps, or blisters
- Pain or burning sensation
- Discharge from the vagina or penis
- Growths or warts
- Abdominal pain
The Body’s Defense System
- Pathogen
- Disease causing agent
- For example, the virus HPV is the pathogen that causes genital warts.
- Disease causing agent
- First line of defense…
- Skin
- Layered to provide intricate web of barriers
- Cracks or breaks in the skin allow pathogens to enter
- Skin
- Second line of defense
- Linings of the body
- For example, mucous membranes in the respiratory tract
- Cilia, tears, ear wax etc. all contain enzymes to destroy invading pathogens
- Linings of the body
- The Immune System
- The body’s natural defense mechanism against a variety of invading substances.
- Must be able to distinguish foreign substances from the body’s own.
- Antibodies
- Formed in response to the body being invaded
Most Common STIs
- Chlamydia: Most frequent
- 5-10 times more frequent than Syphilis or Gonorrhea
- Affects men and women
- If left untreated, can lead to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Asymptomatic most times; urinary burning, vaginal or urethral discharge
- Spread through sexual contact; also by hand from infection site and from mother to fetus
- Caused by bacteria
- Can be treated with a 7 day dose of antibiotics
- Gonorrhea: “The Clap”
- Asymptomatic in early stages; urinary burning, vaginal or urethral
discharge
- Symptoms appear in about 3-5 days.
- Spread through sexual contact, also through hands; can spread to other areas (eyes, anus, rectum); or from mother to fetus
- Caused by bacteria
- Treated with penicillin, however, there are antibiotic-resistant strains
- Asymptomatic in early stages; urinary burning, vaginal or urethral
discharge
- Genital Warts: Venereal warts
- Many asymptomatic; warts range in size from small itchy bumps to large, cauliflower like growths
- Caused by the virus: HPV
- Spread through vaginal, oral or anal genital contact; mother to fetus
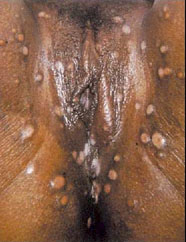
- Herpes
- Caused by a virus
- Symptoms:
- Flu-like: Swollen glands, headache, muscle ache, fever etc.
- Type I: cold sores, fever blisters on lips
- Type II: Genital herpes; painful, shallow sores and blisters on
genitals
- Both types can spread to other parts of the body
- Spread through direct skin to skin contact, oral, anal or vaginal sex, mother to fetus
Herpes
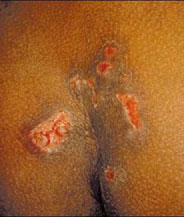
- Syphillis
- Caused by bacteria
- Symptoms:
- 4 stages
- Primary (1-5 weeks)
- Development of a single chancre. Females may develop this outside the vagina, or in the vaginal wall or on the cervex
- Secondary (1-12 months)
- Rash, fever, headache, flu-like symptoms
- Latent (after secondary symptoms disappear)
- Bacteria is still active and infectious
- Tertiary or Late (3-40 yrs.)
- If left untreated, Syphilis can lead to heart damage, central nervous system damage, blindness, deafness, paralysis, mental disturbances, and deat
- Primary (1-5 weeks)
- Can be treated with antibiotic
Syphillis
What To Do If You Have Contracted An STI
- Consult with a health professional
- Take all medication as directed
- Educate yourself about the infection
- Notify sexual partners
- Abstain from sexual contact during an active infection
- Seek support for emotional problem
*note: Statistics from the textbook may be somewhat outdated. Current statistics are from the Center for Disease Control (CDC).
HIV & AIDS
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
HIV and AIDS…. Brief History
- 1981: First reported cases in US
- 1983: Luc Montagnier discovered
- “Retrovirus” (reverses usual flow of genetic information during reproduction)
- A= a virus received from someone else
- I= natural protection against pathogens
- D= a deterioration of the immune system
- S= a group of signs and symptoms that together define AIDS as a human disease
HIV & AIDS
- Prevalence
- 1997: 612,078 reported cases
- 1998: 688,200 reported cases
- 2000: 756,562 reported cases
- ~ 40,000 new cases/year
- A leading killer in U.S.
- 4th leading killer worldwide
- By 1998 > 33 million world wide
- 95% of new cases reported in 1998 from developing countries
AIDS Cases in Adults and Adolescents by Exposure Category and
Race/Ethnicity, Reported through 2000, United States
| Exposure Category
|
White |
Black Not Hispanic |
Hispanic |
|||
| Number |
% |
Number |
% |
Number |
% |
|
| Men who have sex with men (MSM) | 223,470 |
68 |
78,651 |
27 |
48,287 |
35 |
| Injection drug use (ISU) | 39,764 |
12 |
102,492 |
36 |
50,196 |
36 |
| MSM and IDU | 24,958 |
8 |
15,848 |
6 |
7,673 |
5 |
| Heterosexual contact | 16,866 |
5 |
45,601 |
16 |
18,683 |
13 |
| Other/not identified * | 24,551 |
7 |
44,699 |
16 |
14,823 |
11 |
| Total | 329,609 |
|
287,291 |
|
139,662 |
|
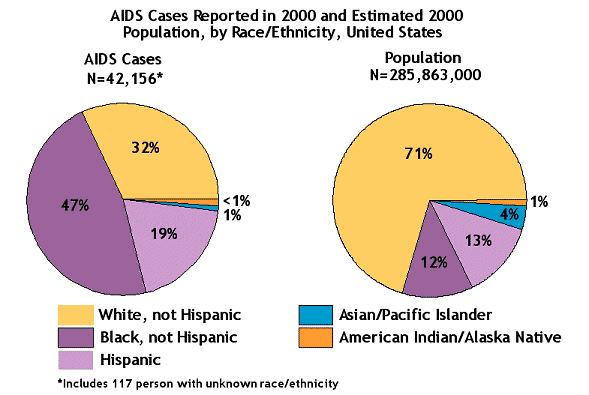
AIDS Chart, Center for Disease Control
HIV Transmission
- HIV IS NOT TRANSMITTED
- Through casual contact
- To humans by insects
- HIV IS TRANSMITTED...
- Through sexual intercourse
- Direct injection with HIV contaminated needles or blood products
- From HIV infected mother to fetus.
- An HIV positive mother has a 30% chance of passing HIV on to her infant. With drugs, this can be reduced to about 8%
- High risk body fluids
- Blood
- Semen
- Vaginal secretion
- Maternal Milk
- *note: The textbook states that maternal mild is not a high-risk body fluid. We know today that it IS a high-risk body fluid. An HIV positive mother breastfeeding her infant has a 25% chance of passing HIV to the infant
- Low or no risk body fluids
- Tears
- Saliva
- Urine
Symptoms Of HIV Infection
- *Will vary greatly depending on individual immune response and infection at work
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Chronic fatigue
- Diarrhea
Diagnosis
- ELISA: screening test
- Testing for antibodies present in the blood
- 99% effective
- Followed by “Western Blot” to avoid false-negative or false-positive results
- Saliva and urine tests are available
- Two home testing kits are now approved by the FDA
- Testing mostly done on a volunteer basis
- HIV testing
- Oregon State Campus Student Health Center
- (541) 737-WELL
- Corvallis Oregon Local Public Health Dept.
- (541) 766-6835
- National AIDS Hotline:
- 1-800-342-AIDS
- Oregon State Campus Student Health Center
Protecting Yourself From STIs
- Avoid high-risk sexual behavior (or abstain!)
- Practice safer sex (i.e., Condoms!)
- Limiting number of partners
- Know your partner and communicate
- See health care provider regularly
- Stay informed about STI’s
Previous Page | Right click this page to print.