Previous Page | Right click this page to print.
Unit 6
Being Psychologically Well
Definition
- Psychological Well-being
- Ability to respond in a positive, healthy manner to life’s challenges
How important is this aspect of health compared to the other five?
Characteristics of the Psychologically Well
- Realistic perspective
- Good opinion of yourself
- Close network of friends
- Sense of purpose
- Ability to handle stress
- Optimistic attitude
When there is an adverse occurrence in your life, you can still perform daily activities. There may be temporary devastation and emotional stress, but there is a confidence that you will make it through. Behaviors aren't drastically changed to cope with problems.
Characteristics of the Psychologically Unwell
- Depression
- Low self-esteem
- Pessimistic
- Poor relationships
- Drug abuse
Individual uses adverse coping mechanisms to deal with problems. (IE: drug use, abusive relationships)
Keys To Psychological Wellness
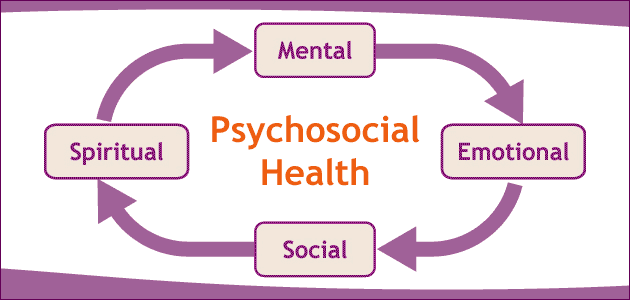
- Mental health (i.e., "thinking")
- How one rationalizes and perceives reality
- Emotional health (i.e., "feeling")
- Being aware of feelings, and expressing it appropriately
- Social health (i.e., "interacting")
- Taking others needs into consideration, having meaningful, intimate relationships
- Spiritual health (i.e., "connecting")
- Creating/discovering meaning and purpose in life. Not easily measured, not necessarily found in religion
Psychosocial Health
Influences On Psychological Wellness
- Internal influences
- Physical health
- It's hard to deal with problems and stressors when an individual is ill. When in good health, there is more energy to deal with problems, and better coping mechanisms are utilized.
- Hormones (e.g., Testosterone)
- Example: Increased testosterone levels are linked with male pattern aggression. Decrease estrogen levels are linked with mood swings in females.
- Heredity
- It is believed that we inherit genes that may determine temperament, and thus affect our coping mechanisms
- Physical health
- External influences
- Environmental influences
- Family, socio-economic status, education, culture, religion
- Social influences
- School, TV, movies, culture, church
- Maturation
- Life experience
- Environmental influences
Explore
What are 2 influences (internal or external) that are currently impacting your level of psychological wellness?
Key Indicators Of Psychological Wellness
3 things we will look at to help determine psychological wellness
- Self Concept
- Attribution Styles
- Locus of Control
Self Concept
- Defined: one’s view of oneself - Physically, mentally, emotionally, socially
- Components
- Self-esteem - Developed over time
- Self-Evaluation of oneself (self-regard, self-worth)
- Self-efficacy
- Perceptions about your ability to act appropriately or successfully in a given situation
- Influence on health
- Blueprint for how one deals with life experiences
- How does self-concept effect behavior?
Attribution Styles
- Defined:
- How people explain the events in their lives
- How people account for successes and failures
- Pessimistic explanatory style
- Leads one to expect the worst
- Optimistic explanatory style ie: Self-fulfilling prophecy, whether
you expect success or failure, you are probably right.
- Leads one to expect the best
Locus of Control
- Defined: one’s belief in his or her power to bring about a certain outcome
- External vs. Internal
- What is the influence on behavior?
- External: May lead one to blame others, set up negative consequences
- Internal: Gives feeling of greater control over consequences
- Individuals may fluctuate in locus of control, but probably lean one way or the other
When Psychological Problems Begin
- Psychological disorders
- Defined: negative mental reactions that compromise health of themselves and those around them.
- Individuals may experience a decline in rational thinking, can distort "perception" of reality
Depression
- Defined:
- Severe disturbance in mood
- Characterized by perceptions of hopelessness, helplessness and mental exhaustion
This is not just "I feel down". This is a full scale tumble into a void where there seems no escape from these feelings of hopelessness, helplessness and exaustion.
- 2 major types
- Endogenous (e.g., neurochemicals)
- Exogenous (e.g., Life events)
- Treatment
- Therapy (counselor, therapist)
- Antidepressant drugs (many options, but requires professional guidance)
- Lifestyle choices (IE: avoiding maladaptive coping mechanisms such as drug and alcohol use)
Some are afraid to seek treatment, why?
Stigma
- Depression: Strikes over 17 million Americans.
- Less than 1/2 are treated
- What makes a college more susceptible to depression, anxiety or suicide?
- Break from family, friends, hometown and old social support systems. Emotionally, socially, financially isolated. Pressure to succeed, gain acceptance, function independently.
Anxiety Disorders
- Characterized by persistent feelings of fear, tension and impending doom
- Types
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Persistent symptoms but not tied to recognizable fear
- Phobia
- Dread of specific objects, activities or situations
- Panic Attacks
- Sudden, extreme anxiety reaction with rapid, disabling fits of terror
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Suicide
26,000 of individuals ages 15-24 commit suicide every year. (40,000 all ages) Suicide knows no social, economic or cultural boundaries
Risk Factors
- Depression
- Drug abuse
- Chronic pain/illness
- High stress
- Family history
Achieving Psychological Wellness
- Self-help
- Books
- Friends, support groups
- Professional help
- Psychiatrists (M.D.)
- Psychologist (Ph.D.)
- Social worker (M.S.W.)
- Counselor
Suggestions for Change
- Practice self-talk
- Ask for help if necessary
- Make time for yourself
- Make time for others
- Plan for crisis
- Move your body
- Remember no one is perfect
Resources for YOU…
- Oregon State University local services
- University Counseling and Psychological Services, (541) 737-2131
- Good Samaritan Mental Health, (541) 757-5235
- Benton County Mental Health, (541) 757-6844
Previous Page | Right click this page to print.