Previous Page | Right click this page to print.
Unit 3
Flexibility, Back Health
- 8 out of 10 people will experience low back pain sometime in their lives
- 80% of all low back problems are muscular in origin
Defining Flexibility
The capacity of a joint to move easily through its full range of motion
- Poor flexibility can cause injuries
- Flexibility declines with age
- The answer...STRETCH!
Defining Flexibility
Joint structure dictates its movement
Types of movement:
- Flexion
- Extension
- Hyperextension
- Abduction
- Adduction
- Circumduction
- Rotation
Defining Flexibility
A Training Effect?
- Yes
- Elastic tissue (muscle)
- No
- Non-elastic tissue (joint capsule, ligaments, tendons)
Stretching Techniques
- Ballistic Stretching
- repeated bouncing motion
- invokes “stretch reflex”
- Static Stretching
- slow, gradual lengthening, holding, releasing
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF)
- stretching a muscle group by previous contraction of the same group
Designing Your Program
- Intensity
- mild to moderate tension
- Duration
- 10 to 60 second hold
- Frequency
- at least 3 times/week
- Rate of Progression
- for each muscle group: 3 reps. X 15 sec. to 3 reps. X 60 sec. by unit 8
- Mode
- dynamic range of motion exercises
- choice of stretching method
- full body, activity specific
Guidelines for Flexibility Training
- Don’t overstretch
- Breathe comfortably
- Choose specific exercises
- Limit stretch during warm-up
- Stretch warm muscles
- Avoid contraindicated stretches
Benefits of Improved Flexibility
- prevention of back pain
- improved performance
- injury prevention
- reduction of muscular and mental tension (e.g. yoga)
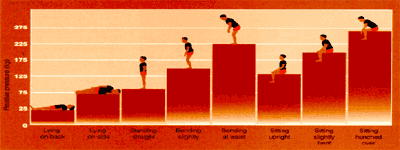
Maintaining a Healthy Back
Poor back health is primarily due to sedentary lifestyles, weak trunk
muscles, and poor posture
Vertebral Column Structure
- Discs - separate, stabilize, & cushion
- Range of motion - greatest in neck & least in upper back
- Thick lower back vertebrae (lumbar) - support the weight of the trunk
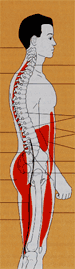
Back-supporting Muscles
- Abdominals - rectus abdominus and obliques, act as “girdle” for pelvis
- Back Muscles - support an upright spine, reduce injury
- Hip Flexors - too tight = poor posture and potential injury
- Hip Extensors - gluteals and hamstrings
Primary Causes of Back Pain
Chronic Disuse
Unhealthy Posture
Lifetime Healthy Back Program
- Correct posture
- sit, stand, walk, and sleep with spine in alignment
- shoulders over pelvis
- sleep on side or back
- lift with your legs, keep weight close
- Strengthening exercises
- include abdominals, back, and hip extensors
- Stretching exercises
- hip flexors, extensors, and back
Previous Page | Right click this page to print.