Previous Page | Right click this page to print.
Unit 3
Muscular Fitness
Types of Muscle Action
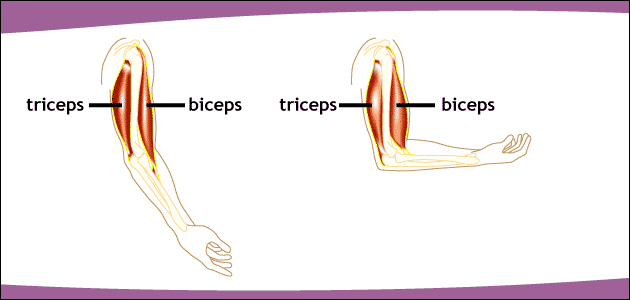
- Concentric
- Muscle shortening
- Eccentric
- Muscle lengthening
- Isometric
- Tension with no movement
Physiological Adaptations
Responses to Resistance Training
- Neuromuscular Response
- nervous and muscular systems
- increase in fibers recruited
- Hypertrophic & metabolic response
- structural changes in fibers
- fibers increase in cross-sectional area
- metabolic changes
Muscle Fiber Types
- Slow-twitch Oxidative (SO)
- oxidative (aerobic) pathway
- postural muscles, low-intensity and long duration training, endurance athletes
- Fast-twitch Oxidative Glycolytic (FOG)
- both oxidative and glycolytic pathways
- Fast-twitch Glycolytic (FG)
- glycolytic (anaerobic) pathway
- gastrocnemius (calf), high-intensity and short duration, speed and power athletes
Benefits of Muscular Fitness
- Musculoskeletal system
- reduces chronic back problems
- improves bone density
- Body Composition
- more lean mass = better % body fat
- Cardiovascular system
- reduces blood pressure
Exercise Prescription
| Strength | Endurance | |
| Frequency | 2-3 days/wk | 2-3 days/wk |
| Intensity | 60-85%1-RM | 50%1 or 15-RM |
| Duration | 3sets/5-7reps | 3sets/12-15reps |
| Rest | 3-5 min/48 hrs | 15-60 sec/48 hrs |
| Mode | Weights | Resistance |
Guidelines for Weight Training
- Warm up and cool down
- Use equipment properly
- Use spotters
- Breathe continuously
- breath holding elevates blood pressure
- Emphasize form, not weight
- entire range of motion (ROM)
- Slow and controlled
Alternate Activities
- Body toning or “body sculpting” classes
- Aerobic classes containing muscular fitness portions
- Step aerobic classes
- Calisthenics
Choose a program which suits your goals, lifestyle, & schedule.
Previous Page | Right click this page to print.