Previous Page | Right click this page to print.
Unit 2
Aerobic Fitness
Percentage of the U.S. Population (18 & older) that Engages in Physical Activity?
- Light to Moderate
- 25%
- Vigorous
- 15%
Aerobic Fitness
Ability of the cardiovascular and muscular systems to provide energy to sustain large muscle group activity over an extended period of time
Aerobic Fitness Body Systems
- Pulmonary System
- Lungs & air passageways
- Cardiovascular System
- Heart, arteries, & veins
- Muscular System
- Muscle fibers
Physiological Responses to Aerobic Training
- Acute Responses
- Ventilation increases
- Cardiac Output increases
- heart rate * stroke volume
- Systolic blood pressure increases
- Chronic Responses
- Resting heart rate decreases
- VO2 max increases
Measuring Aerobic Fitness
the maximal amount of oxygen the body uses to produce energy during exercise which involves use of large muscle groups
Indirect methods
Measures: heart rate response to submaximal exercise or heart rate recovery from exercise
- Bench step test
- Rockport walking test
- Cooper 1.5 mile run/walk test
- YMCA Submaximal Bicycle Ergometer Test
Benefits of Aerobic Exercise
- Cardioprotective mechanisms:
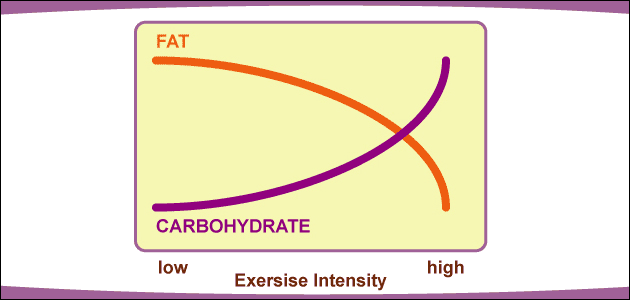
- Enhanced fat metabolism
- Improved lean body mass
- Lowers cholesterol
- Improves circulation
- Decreases blood pressure, if high
- Reduces the heart’s workload
- Slow or reverse the 1% per year age-related decline in aerobic fitness
- Psychological Effects
- Increased self-concept, well-being, and mood
- Decreased stress, depression, and anxiety
Designing an Aerobic Fitness Program
Exercise prescription for Fitness Gains:
- Frequency: 3-7 days/week
- Intensity: 40-85% of heart rate reserve
- Time/Duration: 15-60 min
- Type/mode: enjoyable and convenient
Monitoring Exercise Intensity
- Target Heart Rate (THR)
- varies with age and fitness level
- Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE)
- subjective scale of 6-20
- Talk test
- able to talk briefly = training zone
Guidelines for Aerobic Exercise Sessions
- General Warm-Up - prepares cardiovascular system, increases blood flow, increases elasticity of muscles
- Specific Warm-Up - specific to activity, stretching
- Cool-Down - temp. and HR lower, prevents lower extremity blood pooling, HR < 120bpm, stretch after cool
Previous Page | Right click this page to print.