Previous Page | Right click this page to print.
Unit 2
Introduction to Fitness
WARNING! According to the Surgeon General, physical inactivity may be hazardous to your health.
Components of Physical Fitness
- Aerobic Fitness
- Utilization of oxygen
- Muscular Fitness
- Strength
- Endurance
- Flexibility
- Range of motion
- Body Composition
- Lean and fat components
Three Principles of Training
Progressive Overload Principle
You must subject your body to progressive overload in order to improve physical capacity
Specificity of Training Principle
Only the systems in the body which are specifically stressed by the exercise will adapt & improve
Reversibility of Training Principle
Improvements in fitness are lost if the training is discontinued
Designing a Fitness Program
- Current fitness level assessment
- Identifying goals
- Creating a fitness plan to meet goals
Creating a Fitness Plan
- Frequency: sessions per week
- Intensity: effort level
- Time: duration or exercise time
- Type: mode or form of exercise
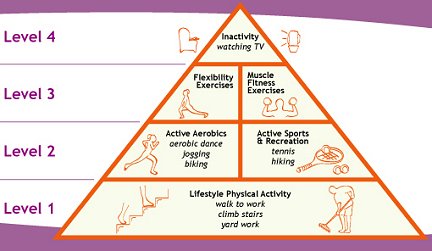
Phases of a Training Program
- Beginning Phase
- Progression Phase
- Maintenance Phase
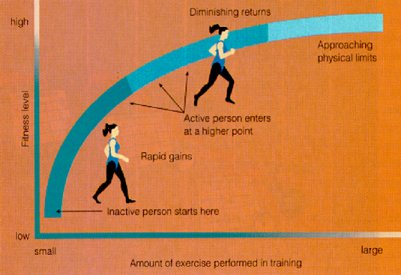
Training Improvement Curve
Exercise Risk Classifications
- Apparently healthy: no symptoms
- Higher risk: 2 or more coronary risk factors or symptoms
- With disease: diagnosed heart disease
Exercise stress test before exercise
Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- High Blood Pressure 140/90
- High Cholesterol > 200 mg/dl total or <35 mg/dl HDL
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Family history
- Sedentary Lifestyle
- Age - 40 men, 50 women
Previous Page | Right click this page to print.