Previous Page | Right click this page to print.
Unit 12
Chronic Disease
Introduction
- Chronic disease
- Any disease that develops over time
- Examples of chronic disease
- Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Osteoporosis
Cardiovascular disease
- Leading cause of death in the U.S.
- Types of CVD
- Artherosclerosis:
- Progressive narrowing and hardening of arteries due to formation of plaque
- Coronary artery disease (CAD):
- Responsible for most heart related deaths
- Myocardial infarction: “Heart Attack”-
- Death of a region of the myocardium do to insufficient blood supply
- Angina pectoris
- MI… but without the heart attack
- Stroke
- Thrombus
- Blood clot attached to plaque on artery wall
- Can be treated with clot-dissolving drugs
- Artherosclerosis:
CVD risk factors
- Cigarette smoking
- 2x the risk
- 2nd hand smoke increases risk by 30%
- Hypertension
- Blood pressure > 140/90
- Elevated cholesterol
- HDL < 45
- “Good”: Picks up cholesterol in the body and delivers it through the blood to the liver, where it is processed and excreted
- LDL > 130
- “Bad”: Delivers cholesterol to cells, responsible for buildup
- What is the desired total cholesterol level?
- HDL < 45
- Physical inactivity
- Obesity
- Contributing factors
- Age
- Sex
- Diabetes
- Stress
CVD Prevention
- Don’t Smoke
- Stay Physically Active
- Maintain Appropriate Body Weight/Comp.
- Diet Low in Fat, Cholesterol, & Sodium
- Monitor Blood Pressure and Blood Cholesterol Levels
- Stress Management
Cancer
- Number 2 Cause of Death in U.S.
- Cancer Defined
- Uncontrollable, abnormal cell growth
- Over 100 different types
- Tumors
- benign = Non-cancerous
- malignant = Cancerous
- metastasis = New cancerous cell growth
Cancer Killers
- Females
- Lung
- Breast
- Colorectal
- Males
- Lung
- Prostate
- Colorectal
| Cancer | Symptoms | Risk Factors | Treatment |
| Lung | chest pain persistent cough bloody sputum |
smoking 2nd hand smoke occupational exposure |
surgery radiation chemotherapy |
| Prostate | pain during urination blood in urine referred back pain |
Male genetics age dietary fat |
surgery radiation chemotherapy |
| Breast | unusual breast lump, swelling nipple discharge breast pain, tenderness |
female age >40 genetics early menarche |
surgery radiation chemotherapy |
| Colo-rectal | rectal bleeding bloody stool irritable bowels |
age > 40 genetics high fat/low fiber diet |
surgery radiation chemotherapy |
Cancer Risk Factors
- Environmental Exposure
- Genetics
- Lifestyle
- diet
- smoking
- stress
Major Cancer-Causing Agents
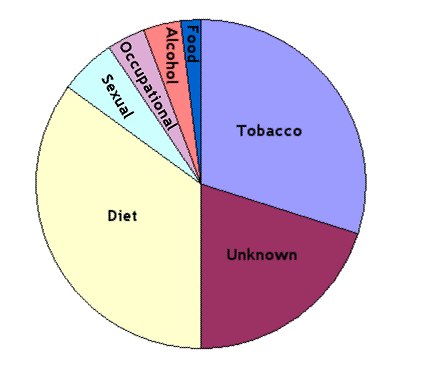
Cancer Prevention
- Change in bowel or bladder habits
- A sore that doesn’t heal
- Unusual bleeding or discharge
- Thickening of tissue
- Indigestions that persists
- Obvious change in a wart or mole
- Nagging cough or hoarseness
More Cancer Prevention
- Avoid tobacco and alcohol
- Anti-cancer diet (i.e., high fiber, low fat)
- Control your weight
- Exercise regularly
- Protect yourself from excessive exposure to sunlight
Introduction to Diabetes
- A leading cause of death in the U.S
- 4th leading cause of death
- Represents a major CVD health risk
- >14 million Americans have diabetes
- 6 million don’t even know it
Defining Diabetes
- Diabetes mellitus
- Abnormally high blood sugar levels
- Also highly susceptible to atherosclerosis, CAD, increase BP, infection, blindness and chronic kidney disease
- Insulin
- Hormone produced in the pancreas that facilitates the transport of glucose from the blood to the muscle, adipose tissue and liver
- Type 1
- Formerly known as insulin-dependent
- Occurs mostly slim children and adults
- Individuals unable to produce insulin
- Type 2
- Formerly non-insulin-dependent
- Resistance to the glucose transport effect of insulin
- Most common in obese individuals over 40
- 90% have type 2 diabetes
Diabetes Risk Factors
- Genetics
- Tendency to develop appears to be present at birth
- Obesity and physical inactivity
- > 20 lbs. Overweight = “at risk”
- Age > 40 are more susceptible to type 2
- Ethnicity
- E.G., African Americans, Latinos and native Americans are all especially prone
Treatment For Diabetes
- Type 1
- insulin
- Diet
- exercise
- Type 2
- weight control
- diet
- exercise
Prevention Of Diabetes
- Maintain normal weight
- Engage in a regular program of aerobic fitness
- Have blood sugar tested beginning at age 45
- Recognize the warning signs
Warning Signs For Diabetes
- Type 1
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Extreme hunger
- Weight loss
- Type 2
- Same as type 1
- Hard-to-heal skin
- Tingling/ numbness in hands or feet
Osteoporosis
- Defined
- Low bone mineral content (BMC)
- Increased susceptibility to bone fracture
- Frequency
- ~25 million Americans--80% are elderly women
Risk Factors For Osteoporosis
- Genetics
- Frame size
- Thin or small frame at higher risk
- Sex
- Women 4 x more likely to develop
- Frame size and estrogen decrease after menopause
- Race
- White & Asian women suffer 2-3 x more
- Age
- Peak bone mass at 15 years
- 1% bone loss a year beginning at age 30
- Low estrogen and testosterone levels
- Physical inactivity
- Inadequate calcium intake
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
Prevention Of Osteoporosis
- Increase physical activity
- Take dietary calcium
- 1200 mg/dl = 4, 8 oz. glasses/day
- Be wary of over exercising
- Keep alcohol consumption moderate
- Don’t smoke
Previous Page | Right click this page to print.