|
|
|
 |
|
| Welcome | Contact | Getting Started | Site Map | Project | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
Topic 10 - Shielding
External Radiation Protection |
Basic Principles
- Minimize exposure time
- Maximize distance from the source
- Shield the radiation source
Distance Effects on Dose Rate
- Radiation
Field Geometry Considerations
- Point Source
- Line Source
- Plane Source
Calculating Fluence and Flux From a Point Source
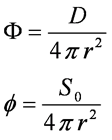
- F = Fluence g/cm2
- f = Flux g/cm2s
- D = total number of photons emitted
- S0 = source strength (photons/s)
- r = distance from source
Point Source Calculations - Photons
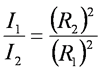
- Dose rate dictated by inverse square law
- I1 = radiation intensity at distance R1 from the source
- I2 = radiation intensity at distance R2 from the source
Example
- 60Co
- 2 photons (1.17, 1.31 MeV)
- Given
3700 MBq source
- What is the exposure rate a 1 m?
- What is the exposure rate at 7.2 m?
Point Source Calculations - Photons
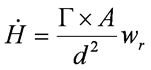
- Dose equivalent rate
- G = specific gamma ray constant
- A = source activity
- d = distance
- wr = radiation weighting factor
- V = velocity of approach to source
- t = total time of exposure
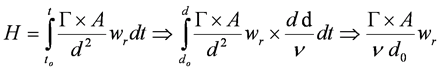
Example
- 10 Ci 60Co source failed to retract into its shield
- Operator walks to source at 1 m/s
- Stops 1 m away, looks for 15 s and leaves at a rate of 2 m/s
- What is the dose commitment?
Line Source (Cember)
- Pipe carrying contaminated waste
- Cl is linear concentration of activity (e.g., Ci/cm or MBq/m)
- Source strength isG
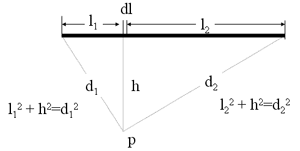
Line Source (Cember)
- Dose rate at point p from small amount dl is
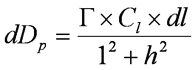
Line Source (Cember)
- Dose rate at point p from total length of pipe is
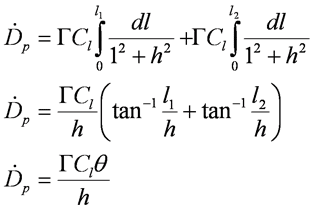
Example
- 24Na in a cooling water line passes through a pipe in an access room 6 m wide
- Door to the room is in the center of the 6m wide wall, 3 m from the pipe
- Activity concentration is 100 MBq/m
- What is the dose equivalent rate in the doorway at point D1 & D2
Example Layout

Line Source Exposure Rate - Photons


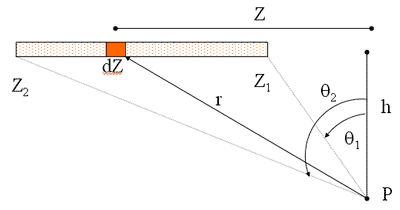
- S = source strength in photons per s per unit line length (cm)
- h = perpendicular distance from point of interest P to the horizontal plane of the source>
- f = flux at point of interest in photons per cm2 per s
- r = distance from source to point of interest, P
- q = angle in radians
- Z2 - Z 1 = line length of source in cm
Ratio of Dose Rates as a Function of Distance Midpoint from a Line Source
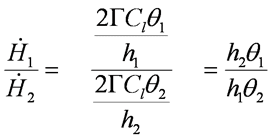
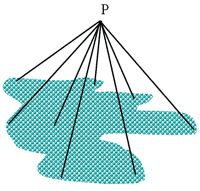
Calculating Flux From Complex Geometries
- Point
Kernel method
- Source broken into many small kernels
- Contribution from each kernel evaluated for a common point
- Contributions are summed
Plane Source
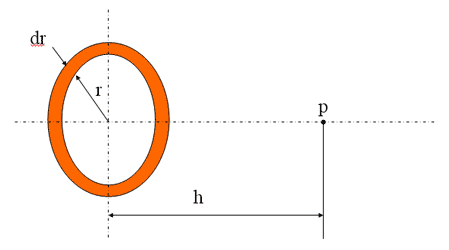
Plane Source Activity
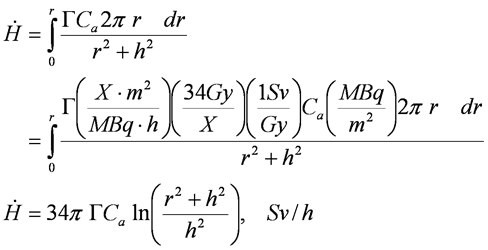
Plane Source Activity, Std Units
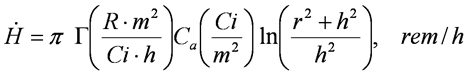
Ratio of Dose Rates as a Function of Distance from a Plane Source
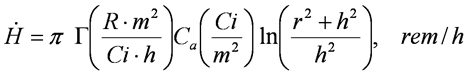

Example
- 50
MBq of 24NaCl solution spilled over a circular area of 50cm
- Find
the dose equivalent rate at
- 30
cm
- 1
m
Volume Source
- Uniformly
distributed activity
- Estimate
based on “effective surface activity”
- Allow
for self-absorption in slab
- Slab
- Thickness
t
- Contains
C v MBq m-3 uniformly distributed activity
- Linear
absorption coefficient of slab is µ
- Observed
intensity at surface due to activity in layer dx at depth x is:
- D(Ca)
= Cvdx·e-µx

Example
- 50 MBq of 24NaCl solution spilled over a circular area of 50cm
- Find the dose equivalent rate at
- 30 cm
- 1 m
Volume Source
- Uniformly distributed activity
- Estimate
based on “effective surface activity”
- Allow for self-absorption in slab
- Slab
- Thickness t
- Contains C v MBq m-3 uniformly distributed activity
- Linear absorption coefficient of slab is µ
- Observed
intensity at surface due to activity in layer dx at depth x is:
- D(Ca) = Cvdx·e-µx
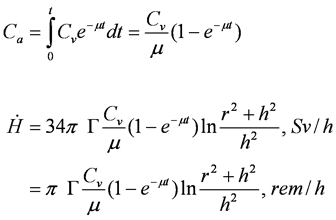
|
|
| Welcome | Contact | Getting Started | Site Map | Project | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |