Topic 11- Radiation Dosimetry
Internal Radiation Protection |
 |
 |
Atmospheric Pathways
- Structure of the atmosphere
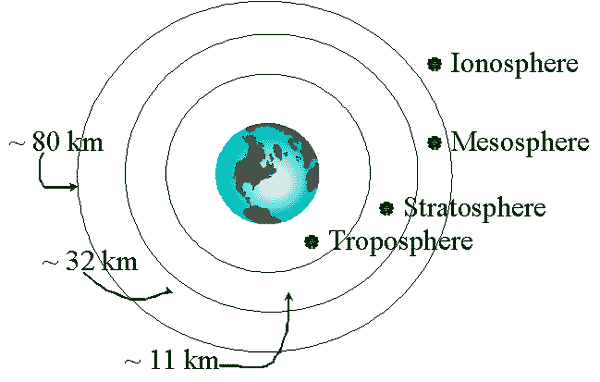
Structure of the Atmosphere
- Troposphere
- varies by season and latitidue
- most weather formed here
- Stratosphere
- dry & cloudless
- no real weather
- lots of ozone
- Mesosphere (warm layer)
- Ionosphere
General Circulation of the Atmosphere
- General circulation proposed in 1735

Prevailing Wind Patterns


Temperature Profile of the Atmosphere

Temperature Profiles of Specific Conditions

- Superadiabatic conditions: vertical motions in atmosphere are accelerated
& atmosphere considered unstable.

- Inversion conditions: temperature increases with height and warm air
over-runs cold; atmoshpere considered stable.
Atmospheric Stability & Stack Gas Behavior


Atmospheric Dispersion and Removal Processes

Dispersion and Removal
- Dispersion
- Removal Mechanisms
- Whatever depletes the plume
- Rainout
- gases/particulates are cause of precipitation
- Washout
- Removal by contact with precipitation
- Dry Deposition
- gravitational settling, impaction
Pasquill Stability Classes (1960s)
| Class |
Description |
| A |
Ectremely unstable |
| B |
Moderately unstable |
| C |
Slightly unstable |
| D |
Neutral Conditions |
| E |
Slightly Stable |
| F |
Moderately Stable |
| G |
Highly Stable |
Relation of Turbulence to Weather Conditions
- A - summer day
- B - sunny & warm
- C - average day
- D - heavy overcast day or night
- E - average night
- F - clear night
- G - inversion, possible fumigation
| Relation of Turbulence Types to Weather Conditionsa,b |
| |
Daytime insolation |
Nighttime conditions |
Surface wind speed
(m s-1) |
Strong |
Moderate |
Slight |
Thin overcast or >= 4/8 cloudinessc |
<= 3/8 cloudiness |
| < 2 |
A |
A-B |
B |
|
|
| 2 |
A-B |
B |
C |
E |
F |
| 4 |
B |
B-C |
C |
D |
E |
| 6 |
C |
C-D |
D |
D |
D |
| >6 |
C |
D |
D |
D |
D |
aFrom Gifford (1996).
bConditions:
A, extremely unstable; B, moderately unstable; C, slighty unstable;
D, neutral (applicable to heavy overcast, day or night); E, slightly
stable; F, moderately stable.
cThe degree of cloudiness
is defined as that fraction of the sky above the local apparent horizon
that is covered by clouds |
|










