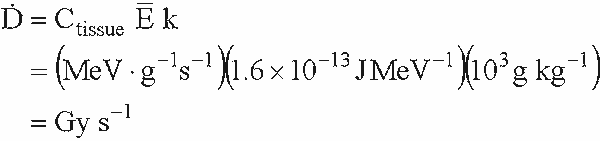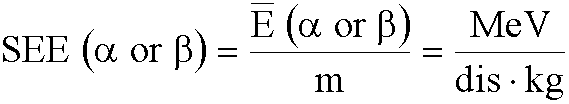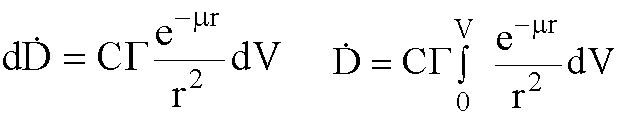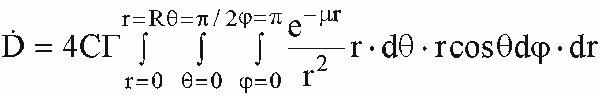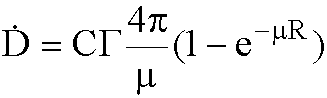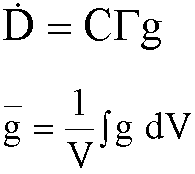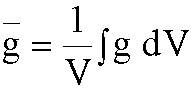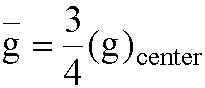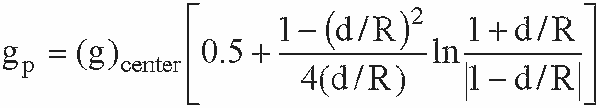Topic 5 - Dose Units
Internally Deposited Radioisotopes |
 |
 |
- Absorbed dose from internal emitters
- Follows directly from definition dose
- For particles with short ranges
- all energy absorbed in tissue :
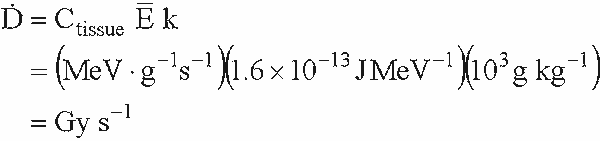
SEE Concept
- Specific Effective Energy
- infinitely large medium
- uniformly distributed radionuclide
- absorbed energy = emitted energy
- “Infinitely large” means
- dimensions exceed the range of radiation
- considers mass of tissue, m:
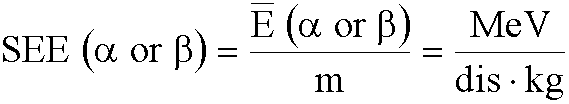
Effective Half-life
- Used to describe residence time of a radionuclide in a tissue or
an organism
- Considers
- radiological (physical) decay (TR)
- biological elimination (TB)
- If biological elimination follows first-order kinetics,
- then can describe with loss rate constant, lB
- related to half life by lB
= (ln 2/ TB)
Effective Loss-Rate Constant
- Biological Loss rate constant, lB
- Sums with radiological loss-rate constant , lR
- lB + lR = lE (effective
elimination constant)
- related to half life by lE = (ln 2/ TE)
Effective Half Life
- Biological (Tb) and Radiological (Tr) half
lives together eliminate the radionuclide from the body faster than
either one alone
- Combined, they are the Effective half life

Where to Find Effective Half Lives (Te)
- Dependent on chemical form
- General guidelines in ICRP 2, ICRP 30
Dose Commitment

Gamma Emitters: Calculating dose at a point, P
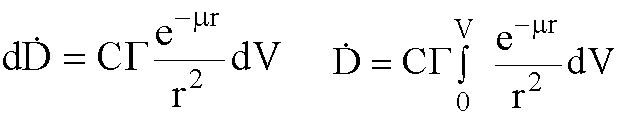
Gamma Emitters for a sphere
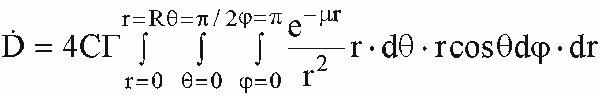
- Integrating with respect to each of the variables, the dose rate
at the center of the sphere is:
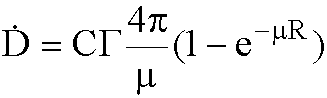
Geometry factors for center of a sphere
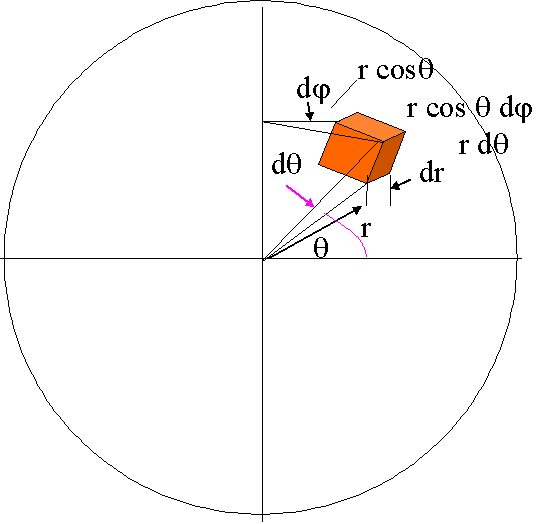
Geometry Factors

- The multiplier is called g, the geometry factor
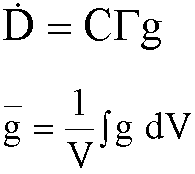
Geometry Factors
- g is for point in a volume of tissue
- what about average dose rate, rather than single point?
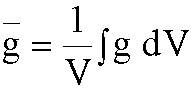
- For a sphere
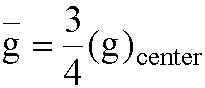
Geometry Factors
- what about at any point a distance d from the center of the sphere
of radius R?
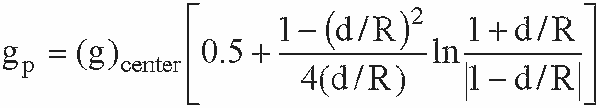
MIRD & Other Dosimetry Methods
- Wait until after biological effects discussion
|