|
|
 |
| Welcome | Getting Started | Resources | Site Map |
Week 1
Gastrointestinal Tracts & Nutrient Utilization |
Instructions for listening to audio clips
- Download the QuickTime Player to listen to the audio files.
- Read the QuickTime Instructions for installation help.
- Download the RealPlayer to listen to the audio files
- Instructions are on the RealPlayer download page
Species Specifics
Time: 6.40
Follow along with the audio...
- Avian species
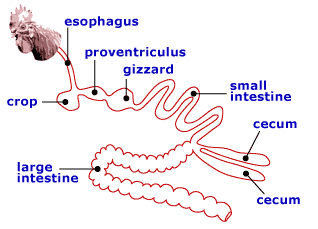
- Figure 1.6 - Poultry GI tract
- Three regions of stomach
- Crop
- Proventriculus
- Gizzard
- Crop
- Temporary storage
- Proventriculus
- Glandular stomach
- Gizzard
- Dense pouch
- Tough, muscular lining
- Grit
- Grinds ingested feedstuff
- Two large ceca
- Combined excretion of urine and feces
- Ruminants
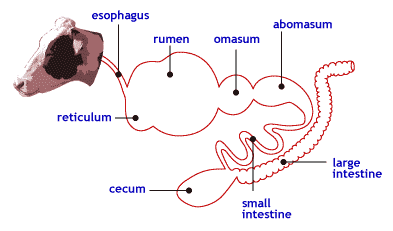
- Figure 1.7 - Ruminant GI tract
-
Anatomy of rumen system
- Figure 1.8 - Ruminant stomach
-
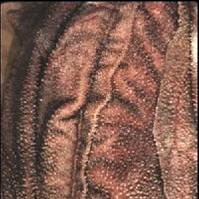
Reticulum
- Figure 1.9 - Interior surface of reticulum
- Honeycomb surface
- Capture dense particles
- Microbial fermentation
- Rumen
- Largest compartment
- Extensive pre-digestive and pre-absorptive microbial fermentation
- Bacteria, protozoa, and fungi
- Population diet and intake dependent
- Lined with papillae
- Increases surface area and absorption
- Figure 1.10 - Interior of rumen
- Omasum
- Figure 1.11 - Interior of omasum
- Membranous leaves in lumen
- Sieve large particles
- Water absorption
- Abomasum
- Glandular stomach
- Largest compartment prior to rumen development
- Unique characteristics
- Reticular or esophageal groove
- Milk directly from esophagus to omasum
- Rumen development
- Stimulated by volatile fatty acids (VFA)
- Lambs – 8 weeks
- Calves – 6 to 9 months
- Rumination
- Regurgitation and remastication
- Eructation
- Emission of fermentation gases
- Reticular or esophageal groove
- Rumen fermentation
- Advantages
- Utilization of fibrous feedstuffs
- Hemicellulose and cellulose digestion
- Utilization of lower quality protein and NPN
- Conversion to higher quality protein
- Production of water-soluble vitamins and vitamin K
- Utilization of fibrous feedstuffs
- Disadvantages
- Reduced utilization efficiency with higher quality feeds
- Reduced yield from digestible energy sources
- High converted to lower quality protein
- Reduced utilization efficiency with higher quality feeds
- Advantages



| |
| Welcome | Getting Started | Resources | SiteMap |