Week 4
Roughages |
 |
 |
Instructions for listening to audio clips
- Download the QuickTime
Player to listen to the audio files.
- Read the QuickTime
Instructions for installation help.
- Download the RealPlayer to listen to the audio files
- Instructions are on the RealPlayer download page
Introduction to Roughages
Text Transcript
Follow along with the audio...
- In U.S., over 50% of feedstuffs fed
- Plant-based feedstuffs
- Terminology
- Forage and herbage
- Plant materials available for consumption by animals
- Roughages
- Higher fibrous carbohydrate content compared to forages
- Terms used interchangeably
- National Research Council
- Minimum CF at 18%
- Maximum TDN at 70%
- Functions
- Provide nutrients
- Maintain and optimize efficiency of GI tract
- Maintain structure, activity, and microbial population
- Use of earth’s resources
- Roughages minimal value to humans
- Consumed by selected species
- Conversion of low-quality to high-quality products
- End-products used by humans
- States
- Types
- Grazed
- Preserved
- Crop residues and by-products
- Note: significant exceptions to following generalizations exist
- Description
- Bulkier feedstuffs; less mass per unit volume
- Low digestible energy
- Low digestibility of other nutrients
- High in fibrous carbohydrates
- Primarily present in cell wall
- Associated with structural components
- Potentially high in lignin
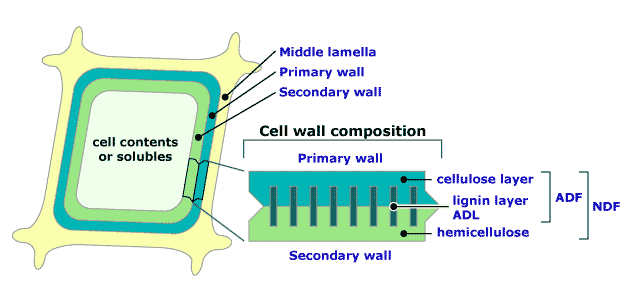
- Nutritional analyses of fibrous carbohydrates
- Crude fiber
- Cellulose and portion of hemicellulose
- ADF
- NDF
- Hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin
- Figure 8.1 - Relationship between components of cell wall and analyses
- Additional components
- Cell contents
- Nonfibrous carbohydrates
- Simple sugars
- Fructose, glucose, and sucrose
- Starch
- Fructosans
- Protein
- True protein
- NPN compounds
- Varies
- Legume content greater than grasses
- Minerals
- Varies by roughage and mineral content of soil
- Legumes higher Ca and Mg contents
- Compared to concentrates
- Higher in Ca, K, and microminerals
- Moderate to low in P
- Vitamins
- Compared to concentrates
- Higher in fat-soluble vitamins
- Good source of B-complex vitamins
- Presence of antinutritional factors
- Examples: alkaloids, cyanogenic glycosides, toxic amino acids,
and/or mycotoxins
- Nutritional value
- Varies
- Plant species
- Proportion of cell contents to cell walls
- Extent of lignification
- Most may be effectively incorporated in at least one type of ration
- Match nutrient requirements with nutrient content
- Appropriate processing and supplementation
- Feeding high-energy feedstuffs with roughages
- Introduction
- Rumen microbial enzymes require for roughage digestion
- Rumen microbial population dependent on feedstuffs
- Diet composition influences digestion of roughages
- Feeding high-energy feedstuffs negative associative effect on utilization
of roughages
- Digestion of roughages
- Cellulolytic species
- Acetate
- Digestion of high-energy feedstuffs
- Propionate
- Lactate
- Lower resultant pH
- pH lower than 6.0 inhibits cellulolytic species
- Decreases utilization of roughages
- Strategies to increase utilization
- Buffers
- Increasing particle size of roughage
- Reducing rate of fermentation of high-energy feedstuff
- Feeding
- Dependent on GI tract
- Microbial enzymes required for digestion of fibrous carbohydrates
- Dependent on site and extent of microbial fermentation in GI tract
- Added to rations of herbivores
- Ratio dependent on animal species and class and cost
- Ruminants
- High utilization efficiency
- Source of fibrous carbohydrates
- Generally, added to rations
- Horses
- Lower utilization efficiency
- Cecum
- Posterior to primary site of absorption
- Coprophagy – consumption of feces
- Improve utilization efficiency
- Used in rations
- Swine and poultry
- Low utilization efficiency
- Limits use in rations
|
 |
 |
|

