Week 1
Nutrients |
 |
 |
Instructions for listening to audio clips
- Download the QuickTime
Player to listen to the audio files.
- Read the QuickTime
Instructions for installation help.
- Download the RealPlayer to listen to the audio files
- Instructions are on the RealPlayer download page
Lipids
-
Text
Transcript
Time: 6.27
Follow along with the audio...
- Chemical composition: organic compounds
- Properties: insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents
- Nutrition - primarily triacylglycerols or triglycerides
- Figure 2.9 – Chemical structure of triglyceride
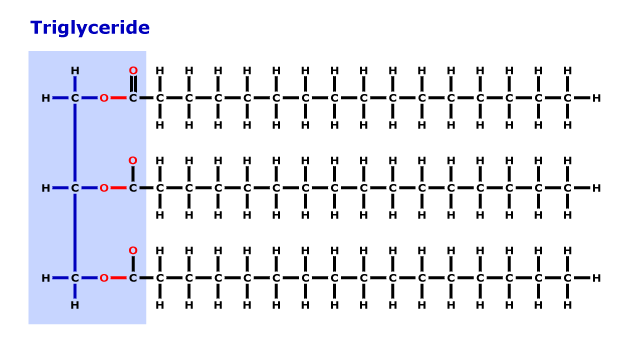
- Three fatty acids (FA)
- One glycerol
- Notation – (#C:#bonds)
- Classifications
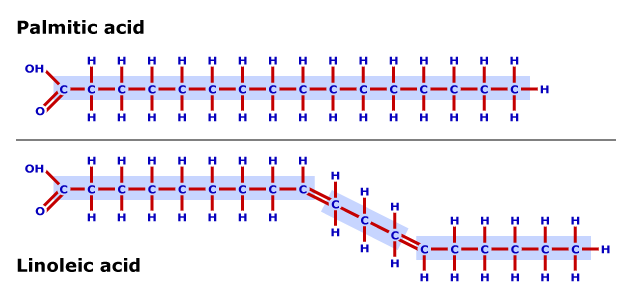
- Chemical structure – saturated or unsaturated
- Figure 2.10 – Chemical structure of saturated fatty acid
- Figure 2.11 – Chemical structure of unsaturated fatty acid
- Physical – fats or oils
- Origin – animal or plant
- Functions
- Energy substrate
- Essential fatty acids
- Dietary essential fatty acids
- Linoleic acid (C18:2) and linolenic acid (C18:3)
- Potentially, arachadonic acid (C20:4)
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Small intestine
- Free fatty acids and monoglycerides
- Additional points for ruminants
- Microbial alterations - level of saturation and position of double
bonds
- Microbial synthesis of fatty acids
- Excess lipids alter rumen fermentation
- Feeding
- Maximum of 6%
- Use of rumen protected – 8%
|


