|
|
 |
| Welcome | Getting Started | Resources | Site Map |
Week 1
Nutrients |
Instructions for listening to audio clips
- Download the QuickTime Player to listen to the audio files.
- Read the QuickTime Instructions for installation help.
- Download the RealPlayer to listen to the audio files
- Instructions are on the RealPlayer download page
Proteins
Time: 7.42
Follow along with the audio...
- Chemical composition: amino acids (AA)
- Figure 2.6 – Chemical structure of amino acid
- Hydrogen, amine, carboxyl, and R group
- All proteins contain nitrogen
- AA and linkages determine protein properties
- Figure 2.7 – Structure of protein
- Functions
- Structure
- Movement
- Digestion
- Metabolism
- Growth
- Defense
- Synthesis
- Regulated by deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- Requires specific AA
- Limiting amino acid
- Twenty AA
- Table 2.1 – Dietary essential and nonessential AA
- Essential
- Animal cannot synthesize adequate amounts; required in diet
- Nonessential
- Animal can synthesize adequate amounts; not required in diet
- Monogastrics
- Digestion – stomach and small intestine
- Mammalian enzymes and other compounds
- Absorption – small intestine
- Amino acids
- Similar AA profile consumed and absorbed
- Ruminants
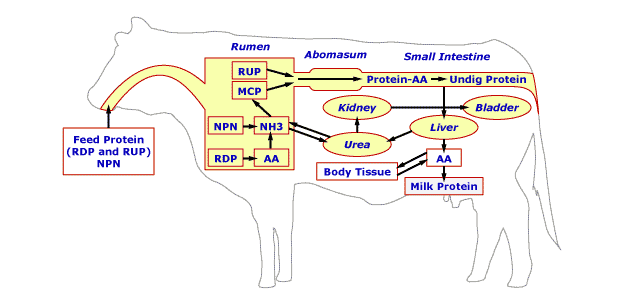
- Figure 2.8 – Protein nutrition in ruminant
- Dietary protein
- Rumen inert or rumen undegradable protein (RUP) or undegradable intake protein (UIP)
- Not changed in rumen
- Digested to AA and AA absorbed in small intestine
- Rumen degradable protein (RDP) or degradable intake protein (DIP)
- Digested in rumen – microbes
- Microbial proteins
- Digested to AA and AA absorbed in small intestine
- Nonprotein nitrogen (NPN) compounds
- Metabolized in rumen – microbes
- Microbial proteins
- Digested to AA and AA absorbed in small intestine
- Microbial protein synthesis
- Substrates – nitrogen and energy
- N recycling
- Requirements
- Monogastrics
- Total protein – true protein
- Limiting amino acids – lysine, methionine, and tryptophan
- Ruminants
- Total protein – True protein and NPN compounds
- Relative amounts
- Limiting amino acids – lysine and methionine

Table 2.1 - Amino Acids
| |
| Welcome | Getting Started | Resources | SiteMap |