|
|
 |
| Welcome | Getting Started | Resources | Site Map |
Week 1
Nutrients |
Instructions for listening to audio clips
- Download the QuickTime Player to listen to the audio files.
- Read the QuickTime Instructions for installation help.
- Download the RealPlayer to listen to the audio files
- Instructions are on the RealPlayer download page
Carbohydrates
Follow along with the audio...
- Chemical composition: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
- Plant origin
- Primary component of feeds and resultant diets
- No specific CHO requirement
- Functions
- Energy substrate
- Fiber
- Forms
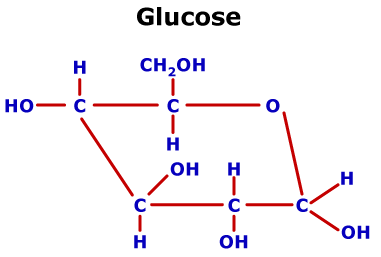
- Monosaccharides
- Examples: glucose, fructose, lactose
- Figure 2.3 – Chemical structure of glucose
- Disaccharides
- Examples: sucrose, lactose, maltose
- Polysaccharides
- Examples: starch and cellulose
- Starch
- Figure 2.4 – Chemical structure of starch
- Glucose molecules – alpha linkages
- Mammalian and microbial enzymes
- Concentrates
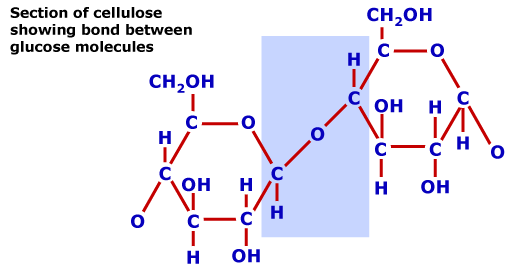
- Cellulose
- Figure 2.5 – Chemical structure of cellulose
- Glucose molecules – beta linkages
- Microbial enzymes
- Forages
- Additional CHO
- Hemicellulose and pectins
- Microbial enzymes
- Monogastrics
- Starch
- Small intestine
- Digestion – mammalian enzymes
- Absorption – monosaccharides
- Horse
- Microbial enzymes
- Utilization of fibrous compounds
- Ruminants
- Sugars, starches and fibrous compounds
- Reticulorumen
- Digestion – microbial enzymes
- Absorption – volatile fatty acids (VFA)
- Acetic, propionic, and butyric
- Used to produce energy substrates
- Intestinal digestion limited
- Lignin
- Not a carbohydrate
- Polyphenolic polymer
- Associated with fibrous feedstuffs
- Indigestible by mammalian and microbial enzymes
- Reduces digestibility of fibrous compounds
- Increases with plant maturity

| |
| Welcome | Getting Started | Resources | SiteMap |